There are no products listed under this category.
Welcome to CM Online Store!
Antibody Drug Conjugate Kits!
AqT bioconjugates coming soon!
 As an alternative to the many years of work—and good fortune—often required to develop a highly selective small-molecule drug, a properly designed delivery system can be used to carry potent antitumor agents. In the mid-1970s, Ringsdorf, a polymer chemist, first proposed the concept of covalently attaching chemotherapeutic agents to water-soluble synthetic polymers.
As an alternative to the many years of work—and good fortune—often required to develop a highly selective small-molecule drug, a properly designed delivery system can be used to carry potent antitumor agents. In the mid-1970s, Ringsdorf, a polymer chemist, first proposed the concept of covalently attaching chemotherapeutic agents to water-soluble synthetic polymers.
Advantages of using polymers to deliver chemotherapeutic agents:
CellMosaic® assists biopharmaceutical companies in developing target-specific small molecule drug conjugates using classical polymer carriers. Human albumin (HA), polyglutamic acid (PGA), N-hydroxymethyl methacrylamide copolymer (HPMA), poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), and PEG are among the polymers widely tested for these applications.
Case Studies:
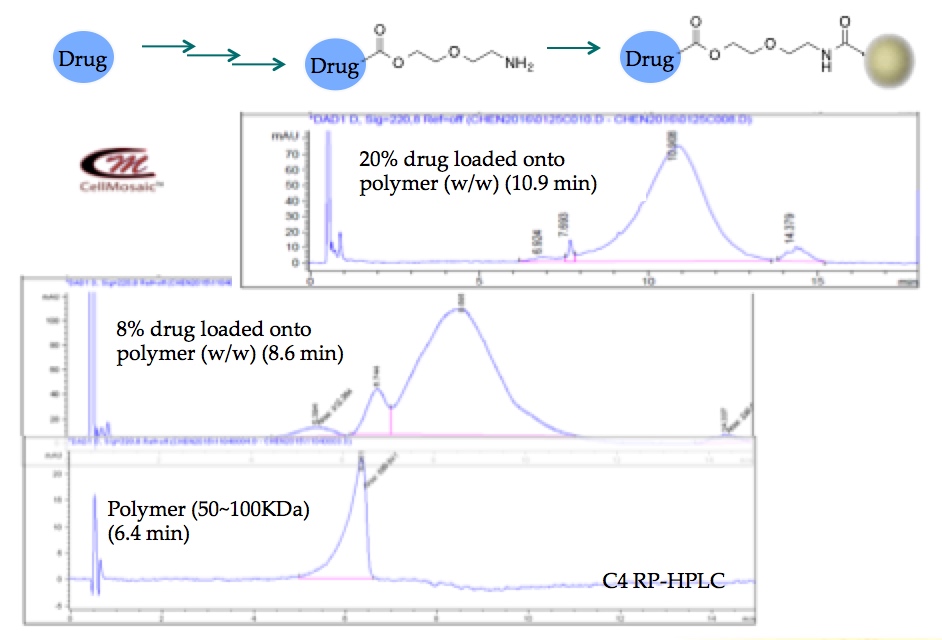
There are no products listed under this category.