AqueaTether® (AqT®) Technologies
Pioneering the Future of Bioconjugation with AqT® Technology
CellMosaic is advancing next-generation bioconjugation solutions through its proprietary AqueaTether® (AqT®) linkers — a revolutionary class of super-hydrophilic, high-loading biomaterials, supported in part by a competitively awarded U.S. Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program (BCRP) Breakthrough Award (2015–2018).
Derived from natural, edible sugar alcohols and engineered with unique chemical architectures, AqT® linkers are designed to overcome the limitations of traditional conjugation chemistries. The technology enables precise and efficient labeling or conjugation of biomolecules with highly hydrophobic small molecules— including fluorescent dyes, biotin, and small-molecule drugs — while preserving biomolecular integrity and solubility. In addition, branched AqT® linkers can be customized to incarease payload capacity, enabling higher loading of detection molecules and delivering significantly enhanced sensitivity and performance in analytical and diagnostic applications.
Beyond research tools, the AqT® platform is transforming therapeutic development. By improving solubility, stability, and biocompatibility, AqT® technology accelerates drug discovery and supports the development of new chemical entities (NCEs) and new biological entities (NBEs) with optimized drug profiles. This versatile platform provides elegant solutions to long-standing challenges such as bioavailability, formulation stability, and toxicity in both small- and large-molecule drug development.
For more information on AqT® technologies in therapeutic applicaitions, please visit www.aqttherapeutics.com
Structure of AqT® Linkers
Sugar molecules are among the most hydrophilic natural compounds because they can form extensive hydrogen bonds as both donors and acceptors. Sugar alcohols, or polyols, are hydrogenated carbohydrates in which the carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone) is reduced to a hydroxyl (-OH) group. They occur naturally in many plant-derived foods, such as fruits and berries, and are commonly used as sweeteners or as building blocks for materials like hydrogels. CellMosaic has developed advanced methods to assemble highly sophisticated AqT® architectures from sugar alcohol monomers.
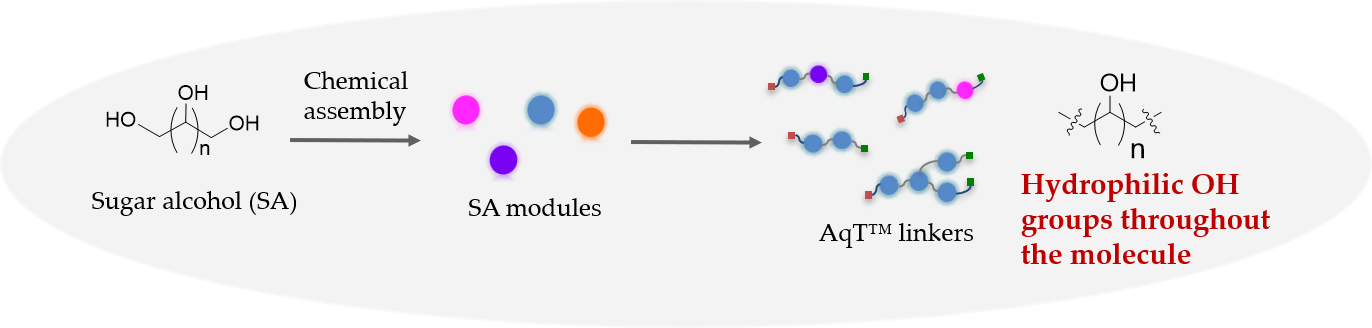
Advantages of AqT® Linkers
AqT® linkers offer several advantages over traditional linkers and polydisperse carrier polymers:
1) Super-hydrophilicity: AqT® linkers are among the most hydrophilic molecules available, providing the exceptional solubility and enabling fine-tuned control of molecular properties after conjugation.
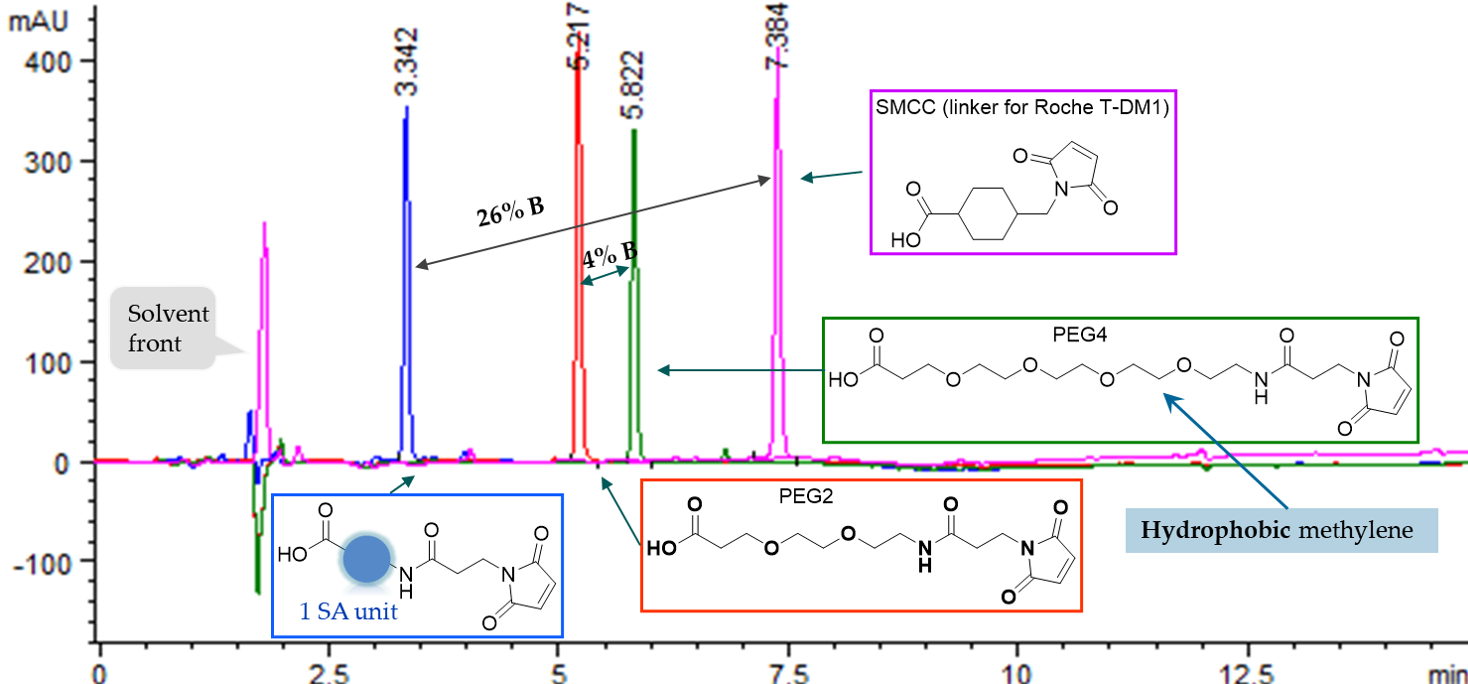
Figure 1. C18 HPLC analysis of AqT® linker and other commercial linkers.
2) Versatility in Crosslinking: AqT® linkers enables the desing of crosslinking reagents with a broad range of functional groups, making them some of the most versatile and tunable molecules available today.
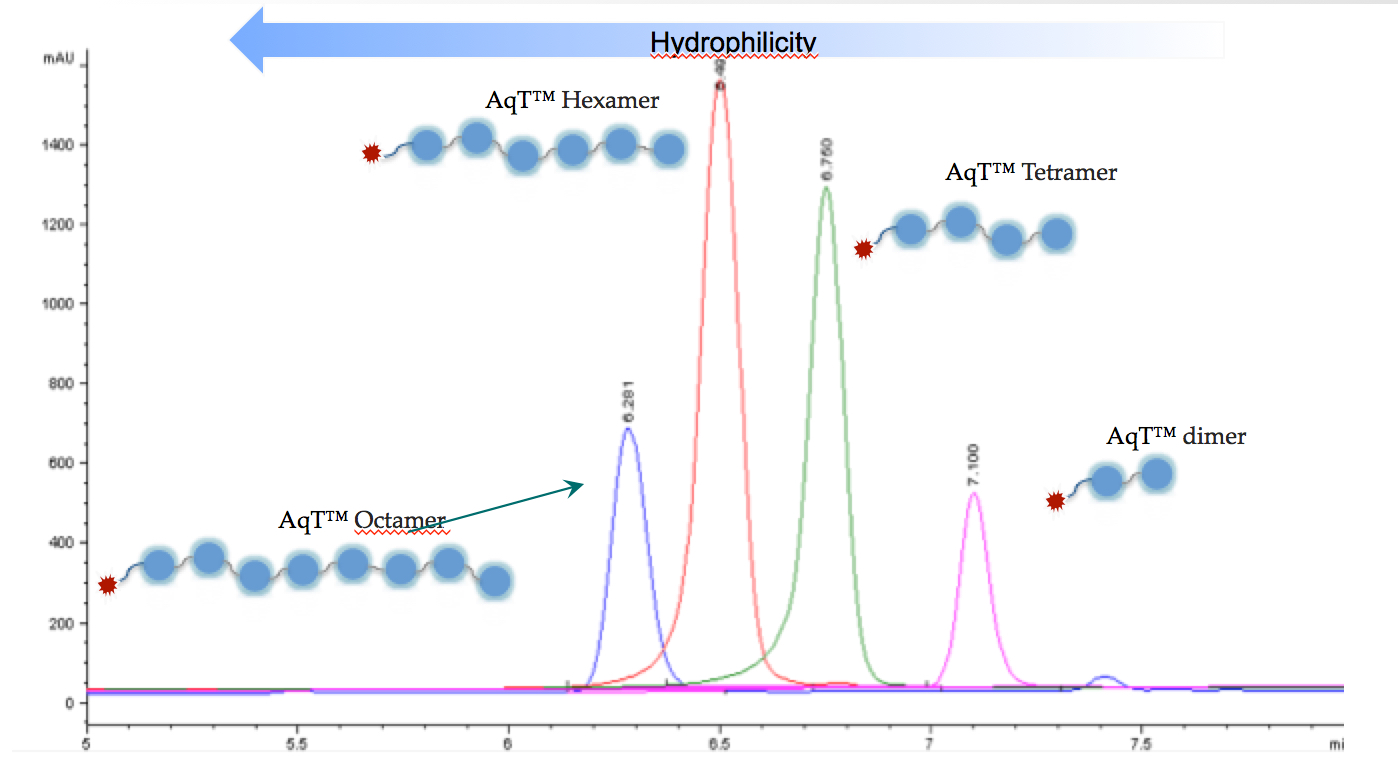
Figure 2. C18 column HPLC analysis of monodisperse AqT® linkers with varying lengths.
3) Enhanced Water Solubility: AqT® linkers significantly improve the water solubility of hydrophobic compounds, allowing conjugation reactions to be carried out in fully aqueous buffers in most cases.
4) Biocompatible: The biopolymer's Properties remain unchanged after AqT®-mediated labeling and conjugation with small molecules (see example of AqT®-biotinylated antibody)
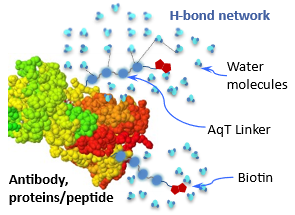
Biopolymers, such as antibodies and proteins/peptides often aggregates and precipitate when labeled with hydrophobic small molecules. AqT® linkers are designed to modify these molecules, enhancing their hydrophilicity and water solubility. The hydroxy (-OH) groups in AqT® form extensive hydrogen bonds with surrounding water, creating a protective microenvironment that shields neighboring small molecules or crosslinking moieties from stacking or interacting with each other. As a result, biopolymers can be labeled with high levels of AqT®-modified molecules without altering their native properties. This AqT®-stabilized hydrogen-bond network also helps protect biopolymers from enzymatic degradation, preserving their biological activity.
- AqT® Linkers Preserve the Native Properties of Biopolymers
- AqT® Technologies are Broadly Biocompatible and Suitable for a Wide Range of Biopolymers
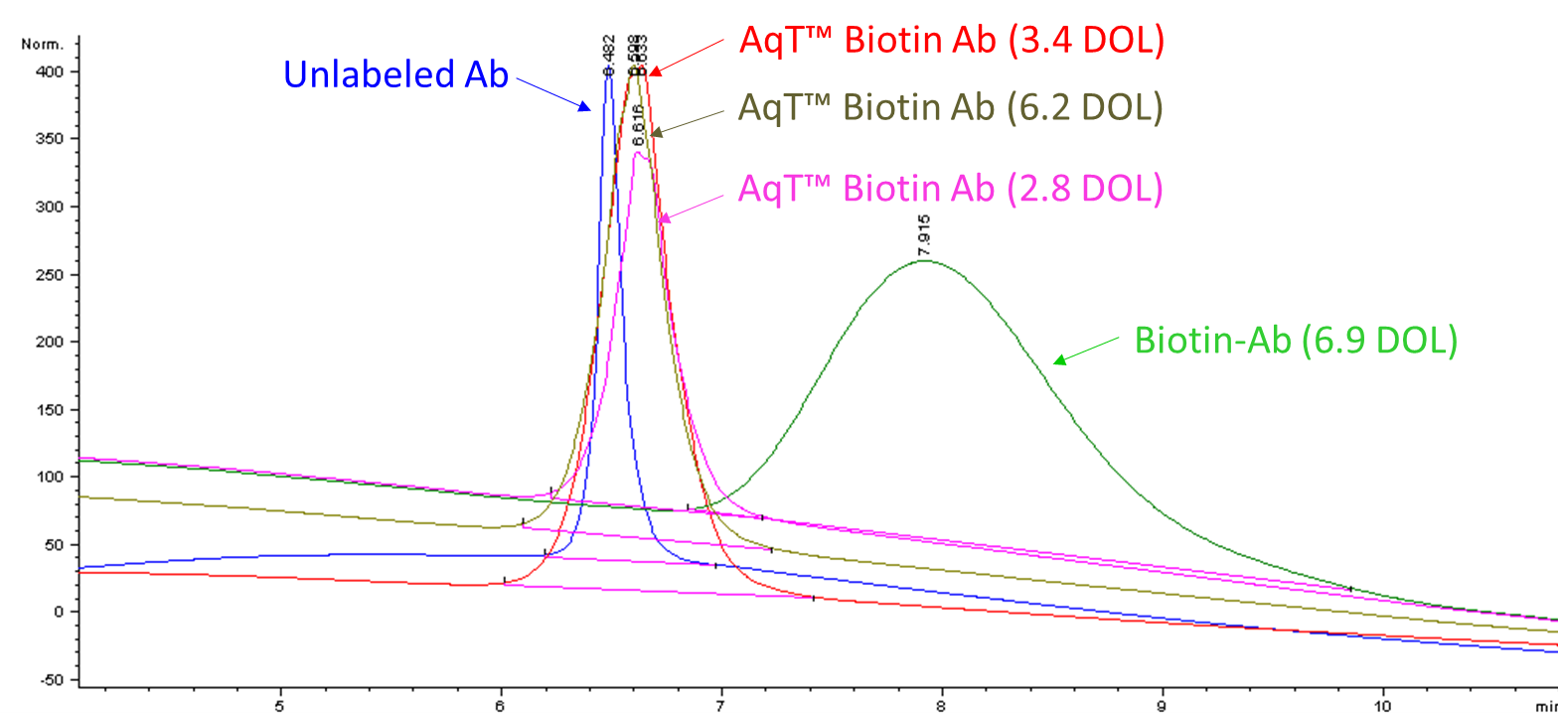
Figure 3. Hydrophobic interaction chromatographic (HIC) analysis of antibody, biotin-antibody (DOL: 6.9), and AqT-biotinylated antibodies with various loadings.
AqT™ Biotin: Retain antibody properties
-
- No changes in hydrophobicity
- Minimal heterogeneity after labeling
Biotin: Change antibody properties
- Increased hydrophobicity (non-specific interaction)
- Highly heterogeneous product
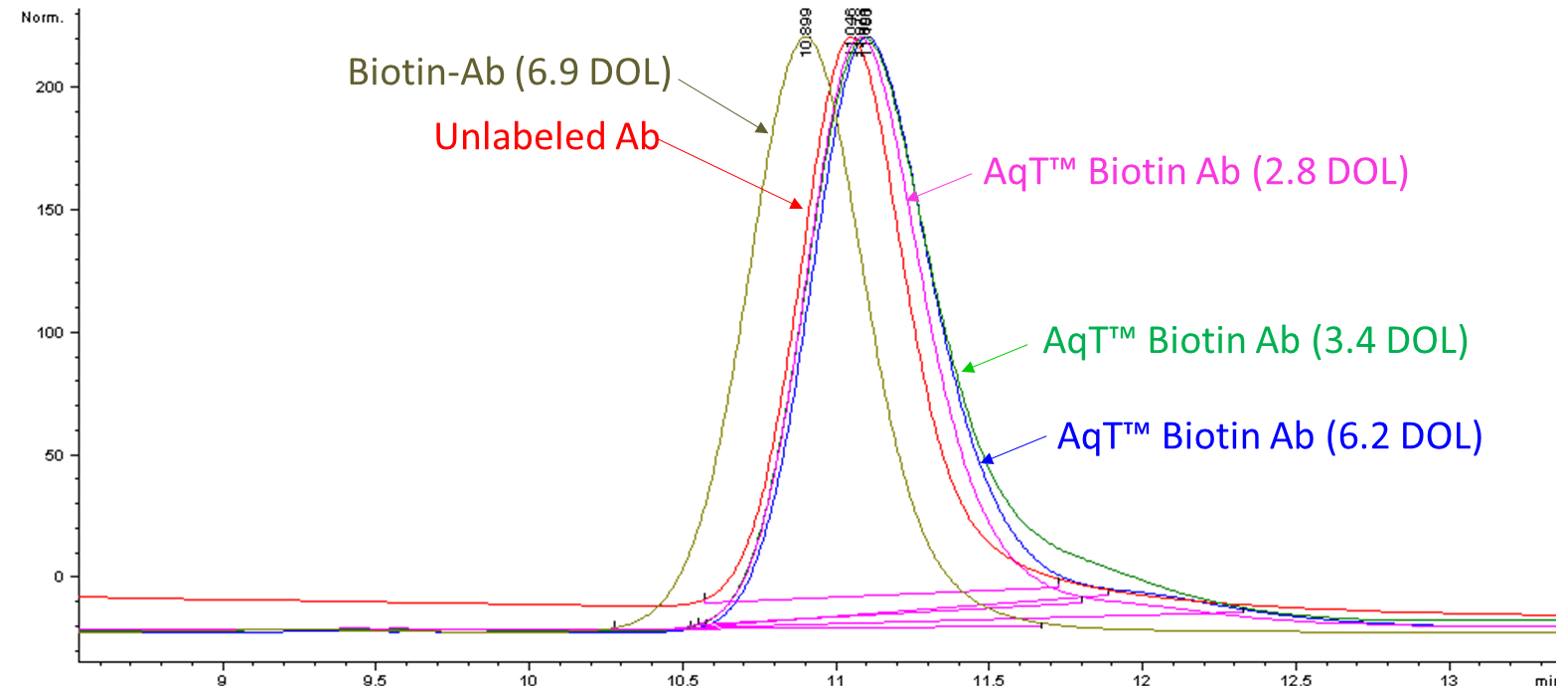
Figure 4. Size exclusion chromatographic (SEC) analysis of antibody, biotin-antibody (DOL: 6.9), and AqT biotinylated antibodies with various loadings.
AqT™ Biotin: Retain antibody properties
- No increase of apparent MW (hydrodynamic volume)
- No increase in aggregation
Biotin: Change antibody properties
- Increased apparent MW (hydrodynamic volume)
- May increase aggregation
Patent and License Restrictions
AqT® technology is protected under WO2013/012961A2, US patent numbers 8907079B2, 9511150B2, US15/281,023, Chinese patent 201280034231.3, Australian patent 2012284055, Japan patent 2014-521744, and equivalent patents and patent applications in other countries, all in the name of CellMosaic, Inc.
We currently offer a limited selection of AqT products for internal research and development use only. The purchase of the AqT Product conveys solely a limited, non-exclusive, non-transferable, non-sublicensable license to use the Product only for the purchaser’s internal research and development purposes. No right or license is granted, either expressly or by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, under any patent, trademark, copyright, or other intellectual property right of CellMosaic, except as expressly stated herein. Any commercial use of the Product is strictly prohibited without a separate written agreement from CellMosaic. Prohibited commercial uses include, without limitation: (a) the sale, lease, licensing, distribution, or other transfer of the Product or any materials derived from or produced using the Product; (b) the sale, lease, licensing, or other grant of rights to use the Product or any materials derived from or produced using the Product; and (c) the use of the Product to perform services for a fee or other consideration for third parties, including without limitation contract research, screening services, or diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
For information regarding commercial licensing, please contact us at info@cellmosaic.com. To explore partnering or collaboration opportunities in the development of AqT therapeutics, visit www.aqttherapeutics.com .
